Finance • 15th Aug 24
Understanding The Concept Tax Management System
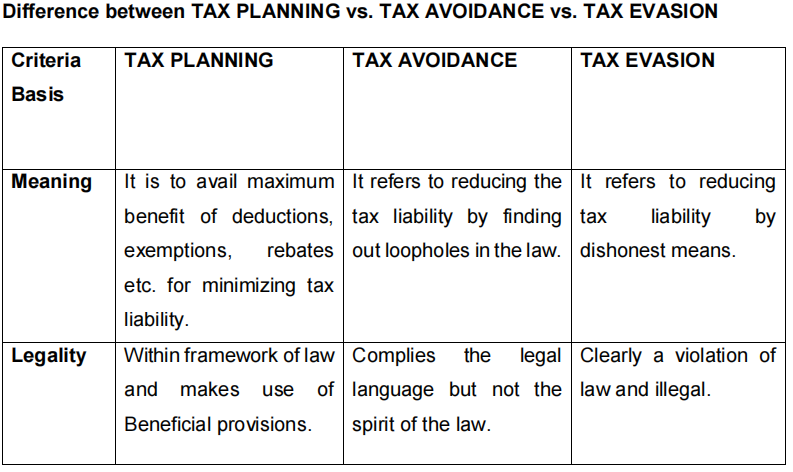
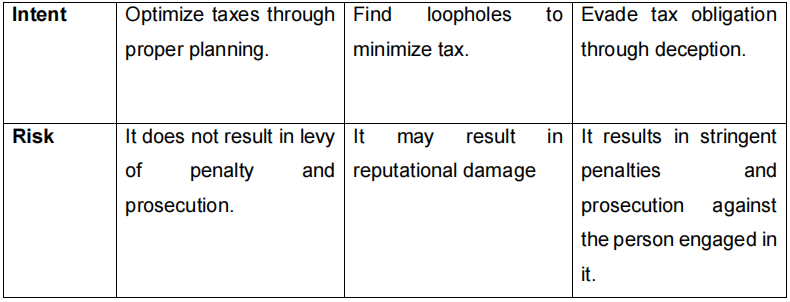
Every Government relies on taxation to generate revenue to run the country. However, there are many ways that people and companies attempt to lower their tax. There are three practices in tax management they are Tax Planning, Tax Avoidance, and Tax Evasion. In this blog, we will explain these tax terminologies in detail.
1. Tax Avoidance
2. Tax Planning
3. Tax Evasion
4. Tax Management
Tax avoidance is the art of evading tax without breaking the law. There is a Small difference between Tax Planning and Tax Avoidance. Tax avoidance outcomes contravenes the object and spirit of the law.
For example, the intention of the law is “Stop, don’t let go” but by using the loopholes of the law assessee claims that this is “Don’t stop, let go”.
Tax Planning is the exercise to minimize the tax and take the advantage of all provisions of Income Tax like deductions, exemptions, relief and rebates.
Tax planning may be defined as an arrangement of one’s financial affairs by taking all advantages like deductions, exemptions, rebates and relief without violating the provisions of the Income Tax and focusing on the spirit behind the law.
Objectives of Tax Planning are:
1. Minimization of tax liability of Assessee.
2. Minimization of Litigation of Assessee.
3. Growth of Economy.
4. Creating employment opportunities in Business.
5. Economic stability of Assessee.
Some Examples for planning:
Making investments that qualify for tax deductions under Section 80C, like Public Provident Fund (PPF), Equity Linked Saving Scheme (ELSS).
Claiming HRA exemption by living in a rented house.
Buying a house property using a home loan makes principal and interest payments eligible for tax benefits under Sections 80C and Section 24. Etc.,
Limitations of planning are:
1. Taxpayer needs a good understanding of tax laws to plan efficiently.
2. Many tax-saving options, such as PPF and ELSS funds, come with a lock-in period, which means the money is blocked for the long term.
3. Tax rules and exemptions may change every year, need to stay updated.
Tax evasion usually involves intentional disregard for certain parts of the law. Tax evasion is when an individual reduces total income by making false claims or withholding information about real income in order to reduce their tax liability. Tax evasion is not only illegal, but it is also immoral, anti-social.
Some of the ways of Tax evasions will be:
1. Fail to pay Tax Dues.
2. False Financial Statement.
3. Using false Documents to claim tax exemptions.
4. Fail to report total Income.
5. Storing wealth Abroad.
6. Benami transactions. Etc.,
Tax management includes regular and timely compliance with the law to help taxpayers avoid interest, fines, penalties and prosecution. The motive of tax management is to comply with the provisions of the law.
Important areas of tax management.
Maintenance of books of accounts.
Audit of books of accounts.
Furnishing the return of income.
Payment of tax.
Documentation and maintenance of tax records.