How Microsoft Makes Money
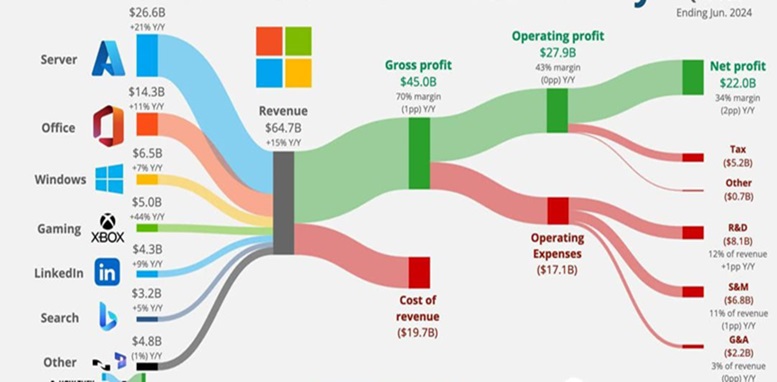
Microsoft Corporation, founded in 1975 by Bill Gates and Paul Allen, has evolved from a software company primarily known for its Windows operating system to one of the largest and most influential technology firms in the world. The company has diversified its offerings significantly, creating multiple revenue streams that contribute to its financial success. This comprehensive exploration details how Microsoft makes money, focusing on its key business segments, products, and strategies.
1. Core Business: Software Sales
1.1 Windows Operating System
Microsoft’s Windows operating system has been a cornerstone of its business for decades. While the dominance of Windows on personal computers has decreased somewhat due to the rise of mobile and alternative operating systems, it remains a significant source of revenue.
- Licensing Fees: Microsoft generates revenue by licensing Windows to device manufacturers, who pre-install it on their computers. This model ensures a steady stream of income from OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) partners.
- Enterprise Licensing: Businesses often opt for volume licensing agreements to equip their employees with Windows. Microsoft offers various licensing options tailored to the needs of organizations, providing additional revenue.
1.2 Microsoft Office Suite
The Microsoft Office suite, which includes applications like Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and Outlook, is another critical revenue driver.
- Subscription Model (Microsoft 365): In recent years, Microsoft has shifted to a subscription-based model with Microsoft 365, which combines Office applications with cloud services such as OneDrive and Teams. This approach generates recurring revenue and fosters customer loyalty.
- Standalone Licenses: Although the subscription model is dominant, Microsoft still offers one-time purchase options for Office. This flexibility caters to users and businesses that prefer not to commit to a subscription.
2. Cloud Computing: Azure
One of the most significant growth areas for Microsoft is its cloud computing platform, Azure. As businesses increasingly shift to cloud infrastructure, Azure has become a vital revenue stream.
2.1 Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Azure offers businesses the ability to rent computing power, storage, and networking capabilities:
- Virtual Machines: Companies can deploy virtual machines to run applications and services without investing in physical hardware. This flexibility allows for scalability and cost management.
- Storage Solutions: Azure provides various storage options, enabling businesses to store and manage data efficiently.
2.2 Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Azure also offers PaaS solutions that allow developers to build, deploy, and manage applications:
- Development Tools: Azure provides integrated development environments and tools, enabling developers to create applications more efficiently.
- Database Services: Microsoft Azure offers various database services, including Azure SQL Database and Cosmos DB, catering to different application needs.
2.3 Software as a Service (SaaS)
Microsoft’s cloud offerings extend to SaaS products, with Microsoft 365 being a prime example. Other services include:
- Dynamics 365: This suite of business applications covers various functions, including customer relationship management (CRM) and enterprise resource planning (ERP). The subscription-based model for Dynamics 365 contributes significantly to Microsoft's cloud revenue.
3. LinkedIn
Microsoft acquired LinkedIn in 2016 for approximately $26 billion. This strategic move has proven lucrative, as LinkedIn has become a key revenue driver through various monetization strategies:
3.1 Advertising Revenue
LinkedIn generates significant income from advertising, offering targeted advertising solutions to businesses:
- Sponsored Content: Companies can promote their posts to reach a broader audience, allowing them to enhance brand visibility and engage potential customers.
- InMail Advertising: Businesses can send direct messages to LinkedIn users, providing a more personalized marketing approach.
3.2 Premium Subscriptions
LinkedIn offers several premium subscription plans for individuals and businesses, such as LinkedIn Premium and LinkedIn Sales Navigator. These subscriptions provide additional features, such as advanced search capabilities, insights, and networking tools.
3.3 Talent Solutions
LinkedIn’s Talent Solutions segment provides tools for recruiting and hiring, contributing to revenue through services like job postings and recruitment advertising.
4. Gaming: Xbox and Related Services
Microsoft has a strong presence in the gaming industry, particularly through its Xbox brand. This segment has become increasingly important as gaming continues to grow in popularity.
4.1 Xbox Consoles
Microsoft generates revenue through the sale of Xbox consoles:
- Hardware Sales: While hardware sales typically have lower margins, the Xbox ecosystem encourages software and service sales, enhancing overall profitability.
4.2 Xbox Game Pass
Xbox Game Pass is a subscription service that allows users to access a library of games for a monthly fee. This model has proven popular among gamers and drives recurring revenue.
- First-Party Game Releases: Microsoft leverages its studios to release exclusive games for the Xbox platform, enhancing the value of the Game Pass subscription.
4.3 Xbox Live
Microsoft also earns revenue from Xbox Live, an online gaming service that offers multiplayer capabilities, free games, and discounts for subscribers. This service fosters user engagement and loyalty within the Xbox ecosystem.
5. Hardware Sales
In addition to gaming consoles, Microsoft produces various hardware products that contribute to its revenue.
5.1 Surface Devices
Microsoft’s Surface line includes laptops, tablets, and accessories designed to run Windows and Office software seamlessly.
- Premium Pricing: The Surface brand is positioned as a premium product, often commanding higher prices compared to competitors, leading to higher profit margins.
5.2 Accessories
Microsoft also sells various accessories, including keyboards, mice, and webcams. These products complement its software and hardware offerings, contributing additional revenue.
6. Enterprise Services
Microsoft offers a range of enterprise services that cater to businesses looking to enhance their productivity and security.
6.1 Microsoft Azure Active Directory
Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) provides identity and access management solutions for organizations. This service helps businesses manage user identities and secure access to applications, generating revenue through subscriptions.
6.2 Microsoft Endpoint Manager
This service provides tools for managing devices and applications within an organization. Microsoft charges enterprises for using these management solutions, contributing to its overall revenue.
6.3 Consulting Services
Microsoft provides consulting services to help organizations implement and optimize its products. This service model generates additional revenue while strengthening customer relationships.
7. Advertising Revenue Beyond Search
While search advertising remains a major component of Microsoft’s revenue, the company also generates income through other advertising avenues.
7.1 Microsoft Advertising
Formerly known as Bing Ads, Microsoft Advertising allows businesses to display ads across the Microsoft ecosystem, including Bing, Outlook, and MSN.
- Partnerships with Publishers: Microsoft partners with various publishers to extend its advertising reach beyond its platforms, generating additional revenue through display and video ads.
7.2 Native Advertising
Microsoft is investing in native advertising solutions that blend seamlessly with content, providing advertisers with new avenues to engage users while enhancing user experience.
8. Data Monetization and Insights
Microsoft leverages its extensive data capabilities to enhance its products and generate additional revenue.
8.1 Business Intelligence Tools
Microsoft Power BI is a leading business analytics tool that helps organizations visualize and share insights from their data. Subscription fees for Power BI contribute to Microsoft’s revenue while enabling businesses to make data-driven decisions.
8.2 Microsoft Graph
Microsoft Graph provides a unified API endpoint to access various Microsoft services and data. Businesses can leverage this data for insights and automation, with revenue generated from usage-based pricing models.
9. Regulatory Challenges and Competition
As Microsoft continues to expand its offerings, it faces various regulatory challenges and competition that could impact its revenue streams.
9.1 Antitrust Scrutiny
Microsoft has historically faced antitrust scrutiny, particularly regarding its dominance in software markets. Ongoing investigations and regulatory actions could affect its business practices and revenue generation.
9.2 Competition
Microsoft competes with numerous technology companies across various segments, including Google, Amazon, and Apple. This competitive landscape necessitates continuous innovation and adaptation to maintain market leadership.
10. Future Growth Opportunities
Looking ahead, Microsoft has several avenues for growth that could further enhance its revenue generation.
10.1 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI represents a transformative opportunity for Microsoft, with potential applications across its product suite:
- Cortana and AI Integration: Microsoft is focusing on integrating AI capabilities into its existing products, enhancing user experiences and productivity.
- Azure AI Services: By expanding its AI services on Azure, Microsoft can attract more businesses looking to implement AI solutions, driving revenue growth.
10.2 Expansion in Emerging Markets
As internet access expands in emerging markets, Microsoft has opportunities to grow its user base. Tailoring products to local needs and investing in infrastructure could yield significant returns.
10.3 Sustainability Initiatives
Microsoft has committed to being carbon negative by 2030, investing in sustainable technologies and practices. By positioning itself as a leader in sustainability, Microsoft can enhance its brand reputation and attract environmentally conscious consumers.
Conclusion
Microsoft's diverse revenue streams—anchored in software sales, cloud computing, gaming, hardware, and enterprise services—demonstrate its adaptability and resilience in a rapidly changing technology landscape. As the company navigates regulatory challenges and competition, its focus on innovation, strategic partnerships, and emerging markets will be crucial for sustaining growth.
With ongoing investments in AI, cloud services, and sustainability initiatives, Microsoft is well-positioned to capitalize on future opportunities. By leveraging its strengths and responding to market dynamics, Microsoft aims to maintain its leadership in the technology sector while delivering value to users, businesses, and shareholders alike.
