How Google Makes Money
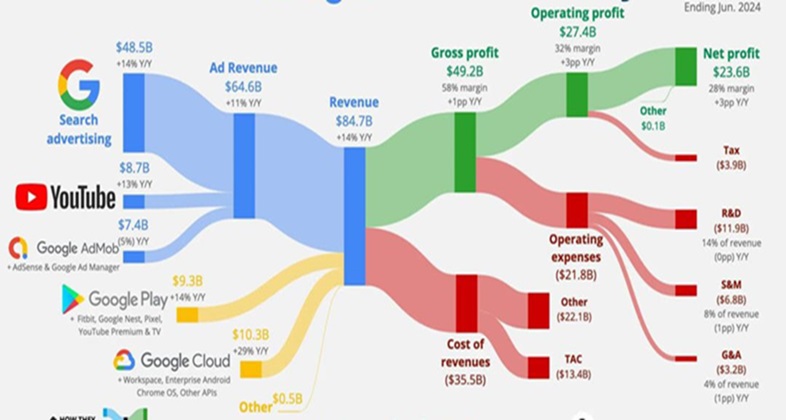
Google, a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc., has grown from a search engine into one of the world's most influential tech giants. With a diverse range of products and services, Google has developed a robust business model that allows it to generate substantial revenue across multiple streams. This exploration provides an in-depth look at how Google makes money, covering its core offerings, advertising business, cloud services, hardware sales, and more.
1. Core Business: Advertising Revenue
1.1 Google Search
At the heart of Google’s revenue model is its search engine. Google Search is the most widely used search engine globally, processing billions of queries each day. The majority of Google’s revenue comes from advertising, primarily through:
- AdWords (Google Ads): Google Ads allows businesses to create ads that appear in search results. Advertisers bid on keywords relevant to their products or services, and when users search for those terms, the ads are displayed. The ads operate on a pay-per-click (PPC) model, meaning businesses only pay when someone clicks their ad. This model allows Google to monetize its vast user base effectively.
- Search Engine Results Page (SERP) Features: Google has integrated various ad formats directly into its search results, such as shopping ads, local service ads, and more. These formats enhance visibility for advertisers while maintaining user engagement.
1.2 Display Advertising
In addition to search ads, Google operates a substantial display advertising business through the Google Display Network (GDN):
- Display Ads: These ads appear on millions of websites and apps that participate in the GDN. Advertisers can reach users based on their interests, demographics, and browsing behavior, which enhances targeting and effectiveness.
- YouTube Advertising: As the owner of YouTube, Google capitalizes on video advertising. YouTube ads can be skippable or non-skippable and can target specific audiences based on user data, making it a powerful tool for advertisers.
1.3 Programmatic Advertising
Google has positioned itself as a leader in programmatic advertising through its DoubleClick platform, now integrated into Google Marketing Platform. This service automates the buying and selling of ad inventory, enabling advertisers to optimize their campaigns efficiently.
- Real-Time Bidding (RTB): Advertisers can bid for ad placements in real-time, allowing for more precise targeting and budget management. This approach ensures that advertisers get the best value for their spending.
- Analytics and Measurement: Google provides tools for tracking ad performance, helping advertisers make data-driven decisions. By offering insights into user engagement and conversion rates, Google enhances the effectiveness of its advertising solutions.
2. Cloud Services
As businesses increasingly migrate to the cloud, Google Cloud has become a significant revenue stream for the company.
2.1 Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
Google Cloud Platform provides a suite of cloud computing services, including:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Businesses can rent virtual machines and storage solutions from Google, allowing them to scale their operations without heavy upfront investments.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Developers can build and deploy applications using Google’s tools, including BigQuery for data analysis and Firebase for app development. This offering attracts a wide range of businesses, from startups to large enterprises.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Google offers productivity tools like Google Workspace (formerly G Suite), which includes Gmail, Google Drive, Docs, Sheets, and more. Subscriptions to these services contribute significantly to Google’s revenue.
2.2 Enterprise Solutions
Google has been increasingly focused on enterprise solutions, providing services tailored for businesses:
- Data Analytics: Tools like BigQuery allow organizations to analyze vast amounts of data quickly. As companies recognize the importance of data-driven decision-making, demand for these services grows.
- Collaboration Tools: Google Workspace has gained traction in remote and hybrid work environments, making it a key player in the enterprise productivity space. The subscription model provides a steady revenue stream.
3. Hardware Sales
Google has expanded into hardware, offering products that complement its software ecosystem. These include:
3.1 Google Pixel Devices
The Google Pixel line includes smartphones, tablets, and laptops. While hardware sales typically yield lower margins than software and services, they are essential for promoting Google’s ecosystem.
- Integration with Services: Google’s hardware is designed to work seamlessly with its services, enhancing user experience and driving software usage.
3.2 Smart Home Devices
Google has ventured into the smart home market with products like Google Nest. These devices include smart speakers, displays, and home security systems.
- Ecosystem Expansion: By offering smart home products, Google aims to create a comprehensive ecosystem that encourages users to engage with its services, such as Google Assistant and Google Home.
3.3 Wearables
Google's acquisition of Fitbit and the development of its own wearable technology signify its commitment to the wearables market. This segment has the potential for growth, especially with the increasing focus on health and fitness.
4. Subscription Services
In addition to advertising and cloud services, Google has introduced various subscription-based offerings.
4.1 YouTube Premium
YouTube Premium allows users to access ad-free content, background play, and exclusive shows. This subscription model diversifies revenue sources and enhances user engagement.
4.2 Google Play Store
The Google Play Store generates revenue through app sales, in-app purchases, and subscriptions. Developers pay a fee to list their apps, and Google takes a percentage of revenue from purchases and subscriptions.
- Digital Content: The sale of digital content, including movies, music, and books, contributes to Google’s revenue through the Play Store. This market is growing as consumers increasingly seek digital entertainment options.
5. Data Monetization
Google’s ability to collect and analyze vast amounts of user data is a cornerstone of its business model. While the company emphasizes user privacy, the data it gathers is essential for its advertising and product development.
5.1 User Insights
Google’s services generate significant data, which it uses to refine its products and advertising algorithms. By analyzing user behavior, Google can enhance targeting, ensuring that ads are relevant to users.
- Personalization: Google employs data to personalize user experiences across its platforms, improving user satisfaction and retention.
5.2 Market Research
Google's extensive data can be used for market research, providing insights into consumer behavior and trends. This information can be valuable for businesses seeking to understand their audiences better.
6. Strategic Partnerships and Acquisitions
Google's growth strategy includes forming strategic partnerships and making acquisitions to bolster its capabilities.
6.1 Partnerships
Google collaborates with various companies to expand its reach and enhance its product offerings. For instance, partnerships with device manufacturers ensure that Google services are integrated into a wide range of products, from smartphones to smart TVs.
6.2 Acquisitions
Google has a history of acquiring companies to strengthen its technology and market position. Notable acquisitions include:
- YouTube: Acquiring YouTube in 2006 allowed Google to dominate the online video space, generating substantial ad revenue.
- DoubleClick: This acquisition bolstered Google’s advertising capabilities, enabling it to offer more comprehensive solutions to advertisers.
- Fitbit: By acquiring Fitbit, Google aims to enhance its presence in the health and fitness sector, integrating data from wearables into its services.
7. Regulatory Challenges and Competition
As Google continues to expand, it faces regulatory challenges and competition that could impact its revenue streams.
7.1 Antitrust Scrutiny
Google has faced scrutiny from regulators worldwide regarding its dominance in search and advertising markets. Antitrust investigations and lawsuits could lead to changes in how Google operates, potentially affecting its revenue.
7.2 Competition
Google faces competition from various tech companies, including Amazon in cloud services and Apple in hardware and services. This competitive landscape requires Google to innovate continually and adapt its strategies to maintain its market position.
8. Future Growth Opportunities
Looking ahead, Google has several growth opportunities to explore.
8.1 Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is a critical area for Google, with the potential to revolutionize its products and services. Google is investing heavily in AI research and development, aiming to enhance search capabilities, improve ad targeting, and create new AI-driven products.
8.2 Expansion in Emerging Markets
As internet penetration increases in emerging markets, Google has opportunities to expand its services and reach new users. Tailoring products to local needs and investing in infrastructure could yield significant returns.
8.3 Sustainability Initiatives
Google is committed to sustainability and aims to be carbon-free by 2030. By investing in green technologies and promoting sustainable practices, Google can enhance its brand reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Conclusion
Google’s multifaceted business model, anchored in advertising but expanded through cloud services, hardware sales, subscription offerings, and data monetization, has allowed it to achieve remarkable financial success. As the company navigates regulatory challenges and competition, its focus on innovation, partnerships, and emerging markets will be crucial for sustaining growth.
With its ongoing investments in AI, cloud computing, and sustainable practices, Google is well-positioned to adapt to the ever-changing technology landscape and continue generating revenue across diverse streams. By leveraging its strengths and responding to market dynamics, Google aims to maintain its leadership in the tech industry while delivering value to users and advertisers alike.
